1. A library does not use encryption when data is transmitted through the network.
Give two reasons why the library should use encryption
Give two reasons why the library should use encryption
[2]
Login to save your answers
/ 2
2. A software development company wants to protect their computer systems and data from
unauthorised access.
Identify two methods of physical security that the company could use to protect their
computer systems
unauthorised access.
Identify two methods of physical security that the company could use to protect their
computer systems
[2]
Login to save your answers
/ 2
3. Identify and describe two software-based security methods that the company can use to protect their computer systems and data
[6]
Login to save your answers
/ 6
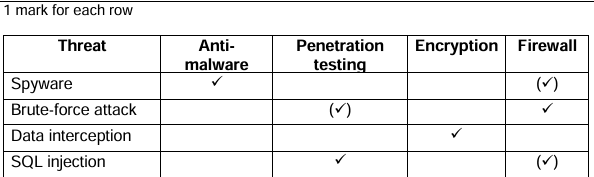
4. Tick one or more boxes on each row to identify all of the methods that can help to
prevent each threat.
prevent each threat.
[4]
| Threat | Anti-Malware | Penetration Testing | Encryption | Firewall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spyware | ||||
| Brute-force attack | ||||
| Data Interception | ||||
| SQL Injection |
/ 4
5. Apart from spyware, brute-force, data interception and SQL injection - name and describe one threat to a computer system.
[3]
Login to save your answers
/ 3
Please login to save your answers and marks.